Engine Wars! F1 vs IndyCar vs Pro Stock vs NASCAR vs Top Fuel
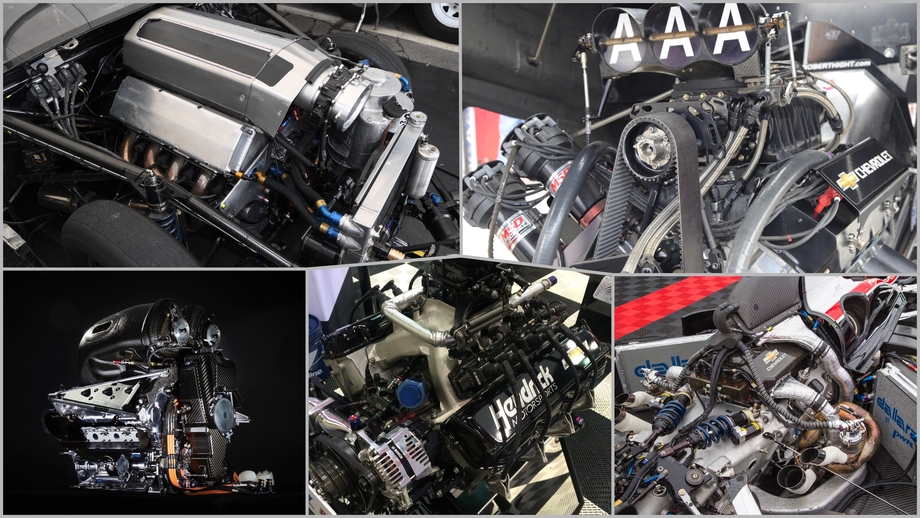
Racing engines have always been shrouded in secrecy because power promises the ultimate advantage. Drivers inherently want enough horses to break the tires lose everywhere on the track. Have too much power? Use less throttle. The motorsport with the most power is obvious to everyone reading these pages, but how far ahead of the competition are we? And what might we learn from the circle-track and road-race engines architectures to make our engines more powerful? We’ve gathered all of the publically available engine specs we could find on F1, IndyCar, Pro Stock, NASCAR, and Top Fuel engines we could dig up.
It’s a collection of information from rulebooks, magazine articles, and the racing series. In some cases, we don’t know certain specs because they are not regulated by the respective sanctioning body, but we’re certainly interested in learning.
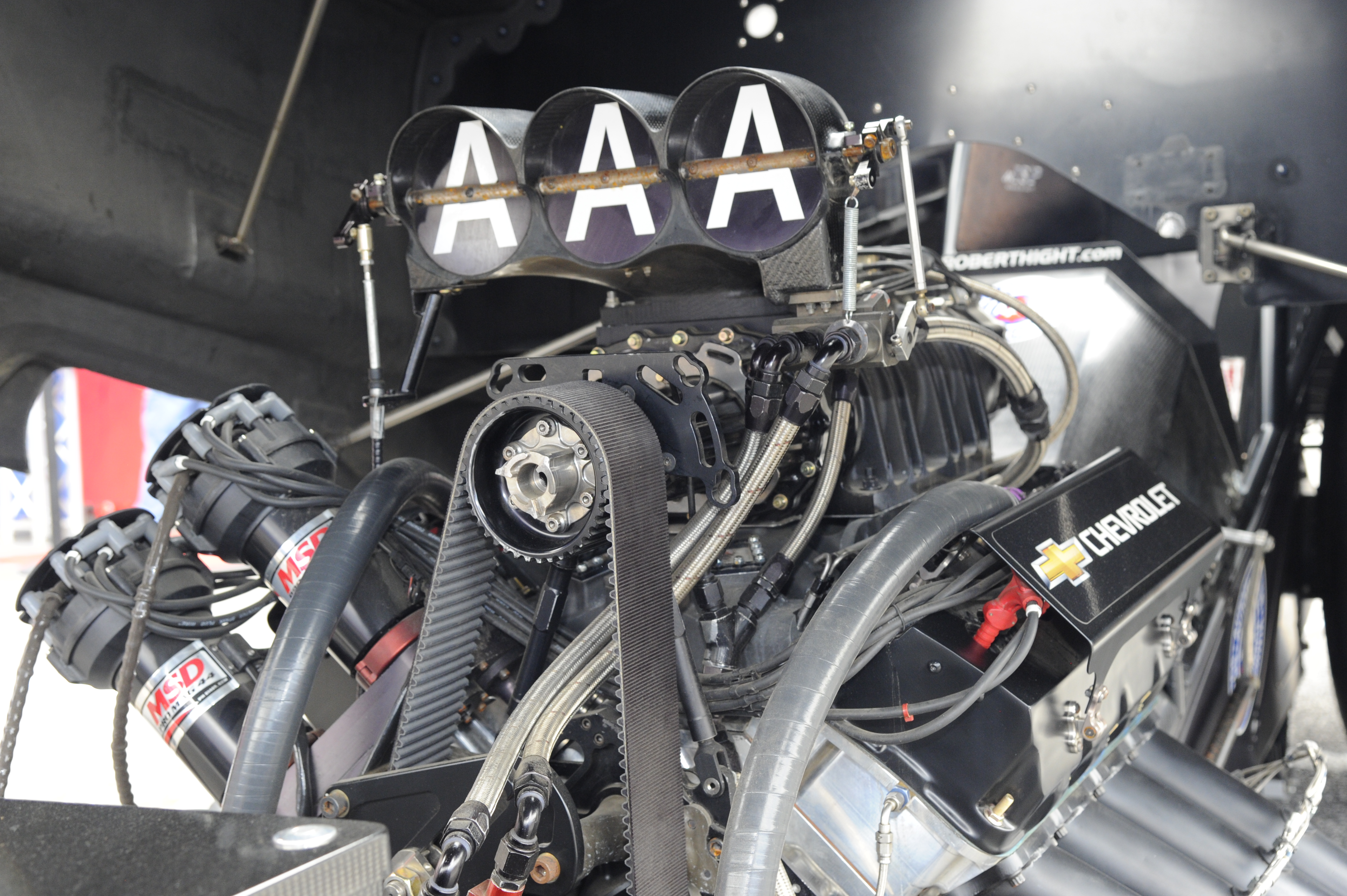
NHRA Top Fuel and Funny Car Nitromethane Engines
Performance: More than 11,000 hp
Engine speed limit: 7,900 rpm (Top Fuel) 7,700 rpm (Funny Car)
Engine design: 90-degree Hemi V-8, with deep-skirt block and cross-bolted main bearing caps
Material: 6065-series aluminum
Maximum displacement: 500 cid (8.2 L)
Bore size: 4.1875 inches +0.004 inch
Maximum bore-center spacing: 4.800 inches
Maximum cam-to-crank centerline: 5.400 inches
Crankshaft material: EN30B USA Timken Steel
Oiling system: Dry-sump oil system permitted
Supercharger: 14-71 roots-type with a billet-aluminum case
Rotor helix: Cannot exceed that of a standard 71-series GM-type rotor group
Rotor material: Billet aluminum with replaceable Teflon or Nylatron strips
Maximum fuel-injector air inlet opening: 65 square
Supercharger inlet: May not exceed 11.750 inches in length and 4.600 inches in width
Supercharger overdrive ratio: 30 to 45 percent
Air volume moved: 3,500 cubic feet per minute (cfm)
 Fuel system: Mechanical multi-port fuel injection
Fuel system: Mechanical multi-port fuel injection
Fuel: Nitromethane, restricted to 90-percent maximum concentration
Fuel pump: Mechanical, engine driven
Fuel pump volume: 115 gallons per minute (gpm) maximum at 8,500 rpm
Fuel burned per run: 14 gallons (18-20 gallons, including warmup)
Intake manifold: Cast magnesium or billet aluminum
Port size: 2.400 inches
Manifold burst panel(s): Mandatory, SFI Spec 23.1
Ignition system: Dual magneto MSD system with 16 sparkplugs
Cylinder heads: Billet aluminum
Combustion chamber size: 200cc
Number of valves per cylinder: Two Intake valve angle: 35 degrees, +- 1 degree Intake valve diameter: 2.470 inches (maximum)
Exhaust valve angle: 21 degrees, +- 1 degree
Exhaust valve diameter: 1.925 inches (maximum)
Valve covers: Must be fabricated steel, titanium, or aluminum
 Camshaft: Roller-lifter style
Camshaft: Roller-lifter style
Camshaft diameter: 60 mm
Typical lift: 0.500-0.525 inch
Lobe separation: 114 degrees
Duration: 303-304 degrees (intake); 300 degrees (exhaust)
Rocker-arm ratio: 1.6:1 to 1.75:1
Exhaust system Top Fuel: Headers must be directed to rear, away from driver. Cannot exceed 16-inches in length measured from the top of the frame rail.
Exhaust system Funny Car: Must be double-tube insulated, not to be laid back more than 40 degrees, and not to exceed more than 83-inches of maximum width from left side of car to the right Maximum header tube outside diameter (O.D.): 2.75 inches. The outside diameter and inside diameter must remain constant to the exit of the header.

NHRA Pro Stock Engine- Chevy Drag Race Competition Engine (DRCE)
Performance: More than 1,400 hp and 800 lb-ft of torque
Engine speed limit: 10,500 rpm
Engine design: 90-degree V-8, with four-bolt steel bearing caps (center three caps are splayed), based on big-block Chevy
Material: Cast-iron (DRCE 2); cast-iron or compacted-graphite iron(CGI) (DRCE 3 and DRCE 4)
Maximum displacement: 500 cid (8.2 L)
Bore: 4.700 inches Stroke: 3.600 inches
Bore-center spacing: 4.900 inches
Cam-to-crank centerline: 5.750 to 7.067 inches
Crankshaft: CNC-machined steel
Oiling system: Dry-sump
 Fuel system: Electronic multi-port Holley fuel injection
Fuel system: Electronic multi-port Holley fuel injection
Throttle body: 25-square-inch Holley unit required on all engines
Fuel: Sunoco SR18 (118 octane) gasoline
Fuel pump: Engine driven or electric, 90 psi maximum pressure
Injectors: 80 or 160-pound-per-hour Holley units, maximum of eight
Fuel burned per run: 1 gallon Intake
Manifold: Billet aluminum
Ignition system: Coil-near plug Holley crank-trigger system with eight sparkplugs
Cylinder heads: Cast T355-T7M aluminum
Number of valves per cylinder: Two
Intake valve diameter: 2.55 inches (approximately)
Exhaust valve diameter: 1.80 inches (approximately)
Valve covers: Fabricated aluminum
Camshaft: Roller-lifter style
Camshaft diameter: 70 mm
Typical lift: 1.10 inch
Lobe separation: 116 degrees
Duration: 280 degrees (intake); 308 degrees (exhaust)
Rocker-arm ratio: 1.75:1 to 2.00:1
Exhaust system: Four-into-one, or tri-Y headers

IndyCar Engine-Chevy Twin-Turbo
Performance: 735 hp
Engine speed limit: 12,200 rpm
Engine design: 90-degree V-6
Engine weight: 248 lbs
Material: Aluminum
Maximum displacement: 134 cid (2.2L)
Bore: 3.74016 inches (95 mm)
Stroke: 2.02 inches (51 mm)
Crankshaft: CNC-machined steel
Oiling system: Dry-sump
Turbochargers: 71-mm-inducer BorgWarner EFR
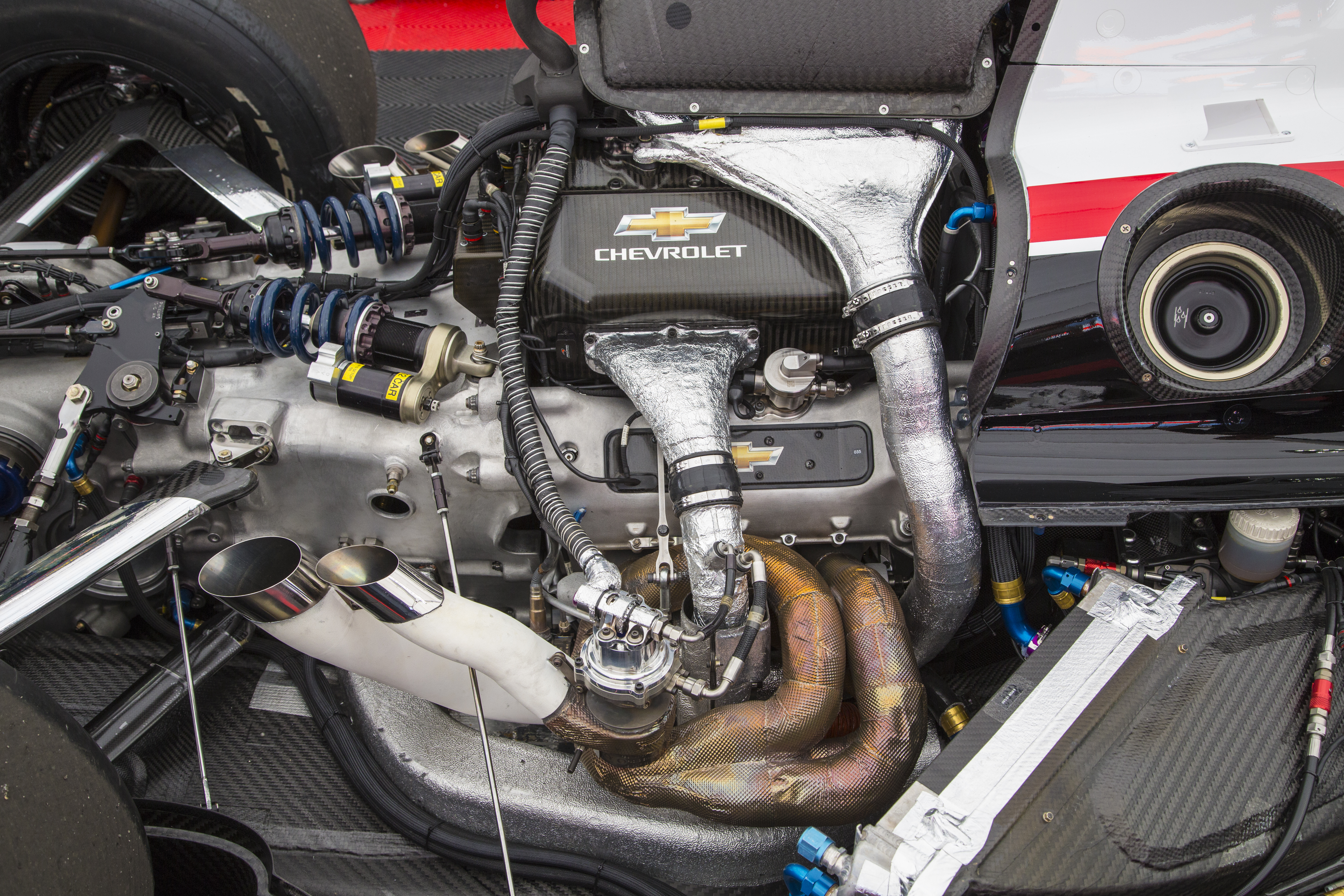 Fuel system: Direct and port electronic fuel injection systems (two injectors per cylinder) controlled by a McLaren Electronics TAG 400i ECU Fuel: E85 (85-percent ethanol, 15-percent race gas)
Fuel system: Direct and port electronic fuel injection systems (two injectors per cylinder) controlled by a McLaren Electronics TAG 400i ECU Fuel: E85 (85-percent ethanol, 15-percent race gas)
Fuel pump: Dual engine-driven injection pumps, plus an electric pump
Injectors: Six in-cylinder (direct) injectors and six port fuel injectors, 4,351-psi maximum fuel pressure Intake
Intake manifold: Composite
Ignition system: Coil-on-plug with six sparkplugs
Cylinder heads: Aluminum
Number of valves per cylinder: Four
Valve covers: Aluminum
 Camshaft: Dual overhead camshaft
Camshaft: Dual overhead camshaft
Exhaust system: Three-into-one headers with dual wastegates

NASCAR Engine-Chevy R07
Performance: 550 to 750 hp (depending on configuration)
Engine speed limit: 10,000 rpm
Engine design: 90-degree V-8, with compacted-graphite iron (CGI) block and four-bolt steel main bearing caps
Engine weight: 525 lbs
Maximum displacement: 358 cid
Bore: 4.185 inches
Stroke: 3.25 inches
Bore center spacing: 4.500 inches
Crankshaft: CNC-machined steel, with 2-inch-diameter main bearings and 1.850-inch-diameter rod bearings
Oiling system: Dry-sump
 Fuel system: Holley electronic port fuel injection systems controlled by a McLaren Electronics TAG-400N ECU
Fuel system: Holley electronic port fuel injection systems controlled by a McLaren Electronics TAG-400N ECU
Throttle body: Holley Fuel: Sunoco E15 (15-percent ethanol, 85-percent race gas) 98-octane
Fuel pump: Engine driven injection pump with electric lift-pumps in tank
Intake manifold: Cast aluminum
Ignition system: Coil-near plug crank-trigger system with eight sparkplugs
Cylinder heads: Cast aluminum
Number of valves per cylinder: Two
Valve material: Titanium
Valve covers: Aluminum Valvetrain
 Camshaft: Flat-tappet style
Camshaft: Flat-tappet style
Camshaft diameter: 60 mm
Typical lift: 0.800-0.950 inch
Rocker-arm ratio: 2.20:1 (but ratio varies)
Exhaust system: Four-into-two-into one headers

F1 Engine-Mercedes Hybrid
Performance: 1,000 hp (engine + electric motor)
Engine speed limit: 15,000 rpm
Engine block design: 90-degree V-6
Engine weight: 320 lbs
Maximum displacement: 98 cid (1.6 L)
Bore: 3.1496 inches (80 mm)
Stroke: 2.0866 inches (53 mm)
Turbocharger: Single turbo, with the compressor mounted at the front of the engine, and the turbine mounted at the rear. An electrical motor generator (MGU‐H) unit is mounted to the turbine shaft between the compressor and turbine wheels to generate electricity, or to be electrically spooled
Oiling system: Dry-sump
Oil type: Must be “engine oil as this term is generally understood”
 Fuel system: Electronic direct-injection Injectors: 220 pound-per hour maximum fuel rate
Fuel system: Electronic direct-injection Injectors: 220 pound-per hour maximum fuel rate
Fuel type: Must be petroleum based, but not contain substances capable of exothermic reaction in the absence of external oxygen Maximum fuel pressure: 7,251 psi
Intake manifold material: Composite
Number of valves per cylinder: Four
Hybrid Power Unit: In addition to the engine there is also a motor generator unit—kinetic (MGU-K) mechanically linked to the powertrain before the main clutch. The maximum torque of the MGU‐K may not exceed 147 lb-ft (200Nm). This unit receives electrical power from the energy storage system on the car, or from the motor generator unit—heat (MGU-H) that’s built into the turbocharger located in the Vee of the engine.






























